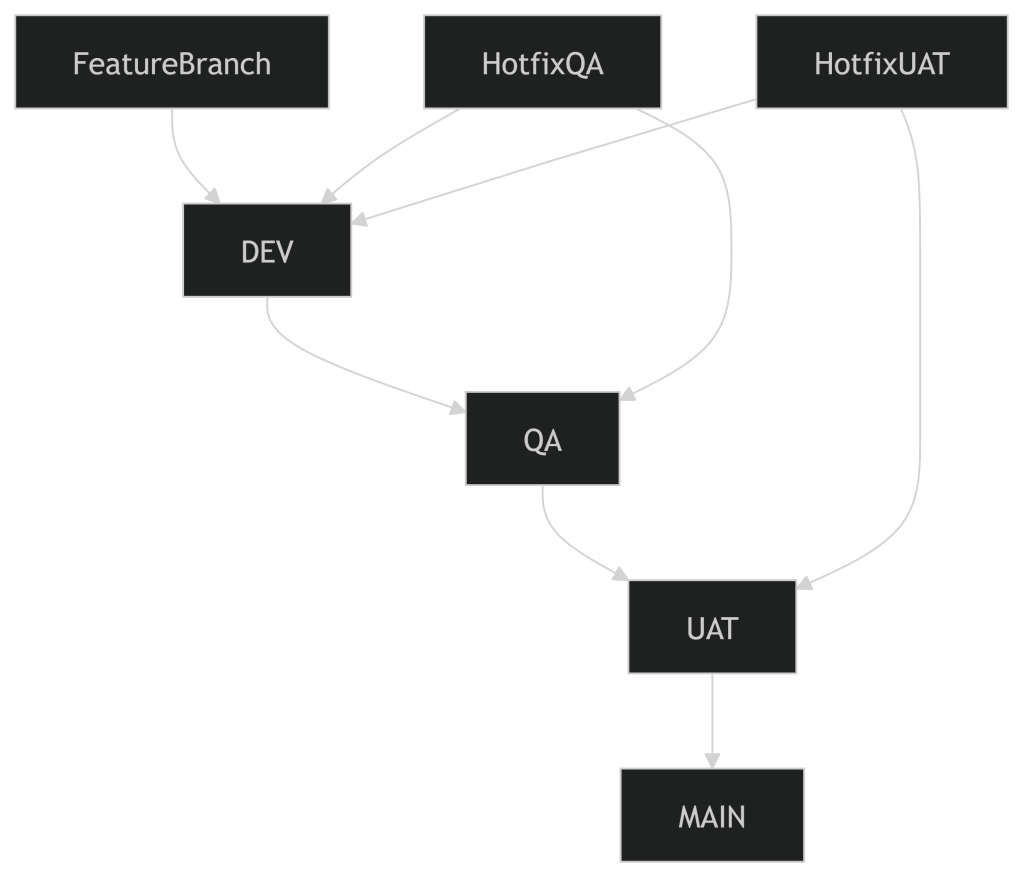
🧩 Branch Roles & Responsibilities
1. DEV Branch
- Purpose: Active development, feature integration, and bug fixes.
- Best Practices:
- Developers work in feature branches off DEV.
- Use pull requests with code reviews before merging.
- Keep DEV stable enough for integration testing.
- Rebase or merge MAIN into DEV regularly to stay up-to-date.
2. QA Branch
- Purpose: Integration testing and bug fixing in a controlled environment.
- Best Practices:
- QA is updated from DEV when a sprint or feature set is ready.
- Bug fixes found in QA should be made in hotfix branches, then merged into both QA and DEV.
- Avoid direct commits to QA unless absolutely necessary.
- Tag builds for traceability.
3. UAT Branch
- Purpose: Final validation by business stakeholders.
- Best Practices:
- UAT is updated from QA after successful QA testing.
- Only critical fixes should be allowed here, ideally via hotfix branches.
- Keep UAT clean and stable for business sign-off.
4. MAIN (or PROD) Branch
- Purpose: Production-ready code.
- Best Practices:
- Only merge into MAIN from UAT after approval.
- Use release tags and maintain a changelog.
- Protect MAIN with branch policies (e.g., no direct commits, required reviews).
- Consider using release branches if multiple versions are supported.
✅ Additional Tips
- Automation: Use CI/CD pipelines to automate testing and deployments between branches.
- Branch Naming: Use consistent naming like
feature/login, hotfix/qa-bug-123, release/v1.2.0.
- Documentation: Maintain a branching policy document for your team.
- Communication: Ensure everyone understands the flow and responsibilities.
Published by SA Otey
Software Engineer
View all posts by SA Otey


You must be logged in to post a comment.